Asset Management Systems (AMS) are comprehensive tools designed to facilitate the systematic tracking, maintenance, and optimization of an organization’s assets throughout their entire lifecycle.
In the pharmaceutical industry, assets encompass a wide range of items, including manufacturing equipment, laboratory instruments, facilities, and intellectual property.
Asset Management Systems in the pharmaceutical industry play a crucial role in ensuring regulatory compliance, maintaining product quality, optimizing operational efficiency, and supporting cost-effective asset utilization.

Let’s look into a detailed overview of how Asset Management Systems are utilized in the pharmaceutical sector:
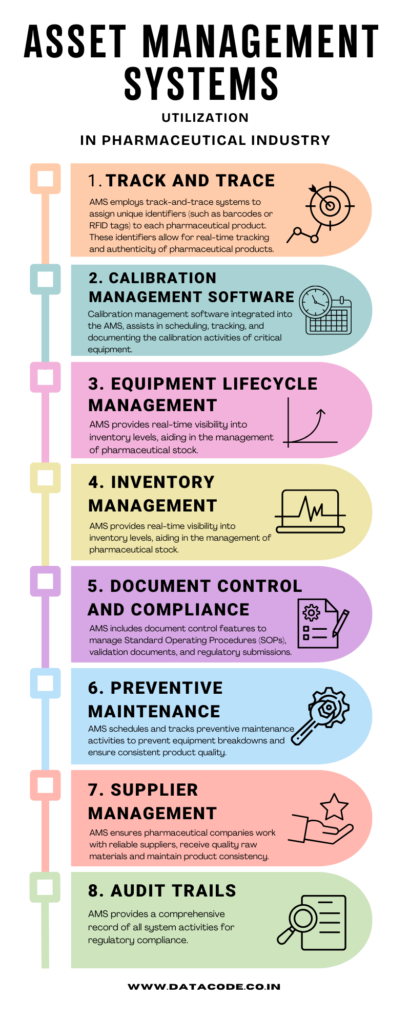
AMS employs track-and-trace systems to assign unique identifiers (such as barcodes or RFID tags) to each pharmaceutical product. These identifiers allow for real-time tracking, ensuring authenticity, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Calibration management software integrated into the AMS assists in scheduling, tracking, and documenting the calibration activities of critical equipment. This ensures that the equipment operates within specified parameters, meeting regulatory standards and maintaining product quality.
AMS helps pharmaceutical companies manage the entire lifecycle of their production equipment. This includes acquisition, installation, preventive maintenance, calibration, and eventual decommissioning. Tracking the status and usage of equipment ensures that it is always in optimal working condition and complies with regulatory requirements.
AMS provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, aiding in the management of pharmaceutical stock. It ensures proper storage conditions, monitors expiration dates, and helps in timely reordering to prevent stockouts or overstock situations. This contributes to cost savings and prevents disruptions in production.
AMS includes document control features to manage Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), validation documents, and regulatory submissions. It ensures that documents are up-to-date, accessible, and readily available during audits, contributing to regulatory compliance.
AMS schedules and tracks preventive maintenance activities for pharmaceutical production equipment. Regular maintenance is crucial to prevent unexpected breakdowns, reduce downtime, and ensure that equipment operates at peak efficiency, meeting regulatory standards.
AMS includes features for managing supplier information, quality audits, and performance tracking. This ensures that pharmaceutical companies work with reliable suppliers, receive high-quality raw materials, and maintain product consistency.
AMS generates detailed audit trails that capture changes made to the system, user activities, and other relevant events. This information is crucial for regulatory audits, allowing organizations to demonstrate compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Hence, Asset Management Systems in the pharmaceutical industry are multifaceted, addressing various aspects such as tracking, compliance, maintenance, and inventory management. The strategic implementation of AMS helps pharmaceutical companies ensure product quality, comply with regulatory standards, and maintain operational excellence in a highly regulated and quality-centric environment.
The pharmaceutical industry, characterized by its strict regulatory environment and high-quality standards, faces several challenges in implementing and maintaining effective Asset Management Systems (AMS). These challenges can impact operational efficiency, compliance, and overall asset performance.
Below are some key challenges faced by asset management systems in the pharmaceutical industry:
The pharmaceutical industry is highly regulated, and compliance with various standards (e.g., GMP, FDA regulations) is crucial. Implementing AMS that meets these standards and ensuring consistent compliance can be challenging due to evolving regulations and the need for continuous updates.
Pharmaceutical companies deal with a diverse range of assets, from manufacturing equipment and laboratory instruments to IT systems and intellectual property. Managing such a diverse portfolio requires a flexible AMS that can accommodate different asset types and their unique requirements.
AMS in the pharmaceutical industry must undergo rigorous validation processes to ensure they meet regulatory standards. Validating the system and maintaining ongoing qualification can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Ensuring the security and integrity of data, especially in AMS that handle sensitive information, is critical. Protecting against unauthorized access, data breaches, and maintaining the integrity of records is a constant concern.
Many pharmaceutical companies use complex enterprise-wide systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) or Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS). Integrating AMS with these systems seamlessly can be challenging, requiring robust interoperability.
Pharmaceutical assets are subject to frequent changes, upgrades, and modifications. AMS must adapt to these changes, ensuring that accurate and up-to-date information is maintained throughout the asset lifecycle.
Implementing effective preventive maintenance schedules is crucial for asset reliability. However, defining the optimal maintenance schedule for each asset, considering production schedules and regulatory requirements, can be complex.
In Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) or Current Good Manufacturing Practice(cGMP) environments, where precise tracking is crucial, traditional tracking methods may be insufficient. Implementing advanced tracking technologies, such as RFID or barcoding, without disrupting GMP operations is a challenge.
Pharmaceutical companies may face resource constraints, including budgetary limitations and a shortage of skilled personnel for implementing and managing AMS. This can hinder the adoption and effective use of sophisticated asset management solutions.
Striking the right balance between restricting access to sensitive information and ensuring that relevant personnel have access to necessary data can be challenging. It requires robust access controls and permissions management.
The rapid evolution of technology may render certain AMS components or features obsolete. Keeping up with technological advancements and ensuring the compatibility of AMS with the latest technologies is an ongoing challenge.
Addressing these challenges requires a strategic approach, involving collaboration between IT, operations, and regulatory compliance teams. Pharmaceutical companies should prioritize selecting AMS that aligns with industry-specific needs and investing in ongoing training and support to ensure successful implementation and sustained effectiveness.
The asset management lifecycle in the pharmaceutical industry involves the systematic management of various assets, ranging from equipment and machinery to intellectual property, to optimize their utilization, maintain compliance, and ensure the quality of pharmaceutical products. Here’s an overview of the asset management lifecycle specific to the pharmaceutical sector:
Objective: Identify the need for new assets, whether they be manufacturing equipment, laboratory instruments, or software licenses.
Activities:
Objective: Ensure that the acquired assets are installed, calibrated, and ready for use.
Activities:
Objective: Optimize asset utilization for manufacturing, testing, and other operational processes.
Activities:
Objective: Ensure that assets remain in optimal working condition and comply with regulatory standards.
Activities:
Objective: Maintain regulatory compliance throughout the asset lifecycle.
Activities:
Objective: Ensure accurate tracking of assets and manage inventory efficiently.
Activities:
Objective: Enhance asset performance through upgrades or replacements.
Activities:
Objective: Safely retire assets that have reached the end of their useful life.
Activities:
Objective: Use data analytics to gain insights into asset performance and make informed decisions.
Activities:
Objective: Implement changes based on insights gained from the asset management lifecycle.
Activities:
Implementing a well-defined asset management lifecycle in the pharmaceutical industry is crucial for maintaining product quality, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, and optimizing operational efficiency. Continuous monitoring, documentation, and improvement of asset management practices contribute to the overall success and sustainability of pharmaceutical operations.
In the pharmaceutical industry, implementing an Asset Management System is a strategic decision that positively impacts operational efficiency, compliance, and cost-effectiveness.
Organizations should carefully select and customize their AMS to meet industry-specific requirements, ensuring optimal asset performance and regulatory adherence.
The well-defined asset management lifecycle in the pharmaceutical sector contributes to the overall success and sustainability of pharmaceutical operations, aligning with the industry’s high standards and stringent requirements.
SS Datacode offers Asset Management Systems solutions to various industries including pharmaceuticals. To know more visit https://datacode.co.in/asset-management/
For inquiries on Track and Trace, Inventory management, and other asset management-related solutions visit our Contact Us page