Serialization and Aggregation in the Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry plays a critical role in safeguarding public health by producing and distributing life-saving drugs and medicines. With the growth of the pharmaceutical supply chain and increasing concerns about counterfeit drugs, the need for effective track-and-trace systems has become paramount. Serialization and aggregation are two key strategies used in the pharmaceutical industry to ensure the authenticity and traceability of pharmaceutical products.
This blog explores the concepts of serialization and aggregation, their importance, regulatory requirements, the technologies involved, process and the challenges faced in their implementation.
Serialization in Pharmaceuticals
What is Serialization?
Serialization is the process of assigning a unique serial number or code to each individual unit of a pharmaceutical product, such as a vial or blister pack. This code is then recorded in a database along with relevant product information, creating a digital footprint for each unit. Serialization allows for the tracking and tracing of individual products throughout the supply chain.
Why is Serialization Important?
Serialization is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps prevent counterfeit drugs from infiltrating the supply chain. By authenticating each unit, it becomes much more challenging for counterfeiters to reproduce and distribute fake pharmaceuticals. Secondly, in the event of product recalls, serialization facilitates rapid identification and removal of affected products, reducing risks to patient safety.
Aggregation in Pharmaceuticals
What is Aggregation?
Aggregation is the process of linking serialized units into higher-level packaging, such as cartons, cases, or pallets. It allows for the association of individual product codes with their corresponding packaging levels. This hierarchical structure enhances traceability and provides a comprehensive view of the product’s journey through the supply chain.
Benefits of Aggregation
Aggregation offers several advantages. It simplifies tracking by consolidating data at different packaging levels, enabling efficient monitoring of inventory, reducing handling errors, and expediting recalls. Aggregated data is especially valuable for wholesalers and distributors who manage large volumes of pharmaceutical products.
Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory bodies, including the FDA in the United States, the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and India’s Directorate General for Foreign Trade (DGFT) have implemented strict serialization and aggregation requirements. These regulations demand that pharmaceutical manufacturers implement serialization and aggregation in their production processes to enhance product traceability and compliance.
Serialization and Aggregation Technologies in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmaceutical companies use various technologies to implement serialization and aggregation effectively. Let’s look into a few technologies below
Barcoding
Barcoding is a common method used for serialization. Each unit is marked with a unique barcode that contains product information. Barcodes are easily scanned and read, making them cost-effective and efficient for tracking individual products.
RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification)
RFID technology employs radio waves to transmit data wirelessly. RFID tags can be attached to pharmaceutical products, allowing real-time tracking and data collection. RFID is often used for aggregation, as it facilitates the association of individual units with higher packaging levels.
Data Management Systems
Effective serialization and aggregation require robust data management systems. These systems record, store, and manage the vast amount of data generated during the process. They play a crucial role in ensuring compliance, traceability, and rapid response to recalls.

Process of Serialization and Aggregation in the Pharmaceutical Industry?
Serialization and aggregation in the pharmaceutical industry are critical processes for ensuring the authenticity, traceability, and safety of pharmaceutical products. These processes involve assigning unique identifiers to individual units of pharmaceutical products and linking them into higher-level packaging. Here is an overview of the steps involved in the serialization and aggregation process:
Serialization:
- Unique Identifiers: The first step in serialization is to assign a unique serial number or code to each individual unit of a pharmaceutical product. This unique identifier is often in the form of a barcode or a 2D data matrix code, and it contains essential product information.
- Data Recording: Each serialized unit’s code, along with relevant product data, is recorded in a centralized database. This database acts as a repository for tracking and tracing information, including details such as the manufacturing date, batch number, expiry date, and product description.
- Labelling: After the unique identifier and product data are recorded, the individual product units are labelled with the assigned code. This label is typically affixed to the packaging of the product, such as vials, blister packs, or bottles.
- Verification: Quality control processes ensure that the serialization codes are correctly applied and recorded in the database. This step helps to identify any errors early in the process and ensures data accuracy.
- Data Management: Robust data management systems are essential to store and manage the vast amount of data generated during serialization. These systems play a vital role in maintaining data integrity, security, and accessibility.
Aggregation:
- Grouping Serialized Units: Aggregation involves grouping serialized individual units into higher packaging levels, such as cartons, cases, or pallets. These higher-level packaging items are also assigned unique identifiers, and they include information about the serialized units contained within.
- Aggregation Data Recording: Just as with serialization, the aggregation process requires recording data associated with higher-level packaging. This data includes the unique identifiers of the individual units contained within the higher-level packaging.
- Labelling: The higher-level packaging, such as cartons or pallets, is labelled with a unique code that links it to the aggregated serialized units. This label often contains an aggregation code or identifier.
- Verification: Similar to serialization, quality control procedures are implemented to verify that the aggregation codes and data are correct, and the correct units are grouped together in the higher-level packaging.
- Data Management: Data management systems play a significant role in storing and managing the data related to aggregation. These systems maintain the hierarchy of aggregated products, making it possible to trace individual units back to their original source.
Implementation Challenges
While serialization and aggregation offer significant benefits, implementing these systems in the pharmaceutical industry is not without its challenges. These include the high cost of technology adoption, the need for collaboration across the supply chain, and potential data security concerns. Companies must navigate these obstacles to ensure the successful implementation of serialization and aggregation.
Conclusion
Serialization and aggregation are essential strategies in the pharmaceutical industry to ensure product authenticity and traceability, protect public health, and meet regulatory requirements. By assigning unique codes to each unit and linking them into higher packaging levels, pharmaceutical companies can enhance supply chain security, streamline operations, and respond efficiently to recalls.
As technology continues to evolve, serialization and aggregation systems are likely to become even more sophisticated, offering further benefits to the pharmaceutical industry. Pharmaceutical companies must adapt to these changes to maintain their commitment to quality, safety, and patient well-being in the ever-evolving landscape of drug production and distribution.
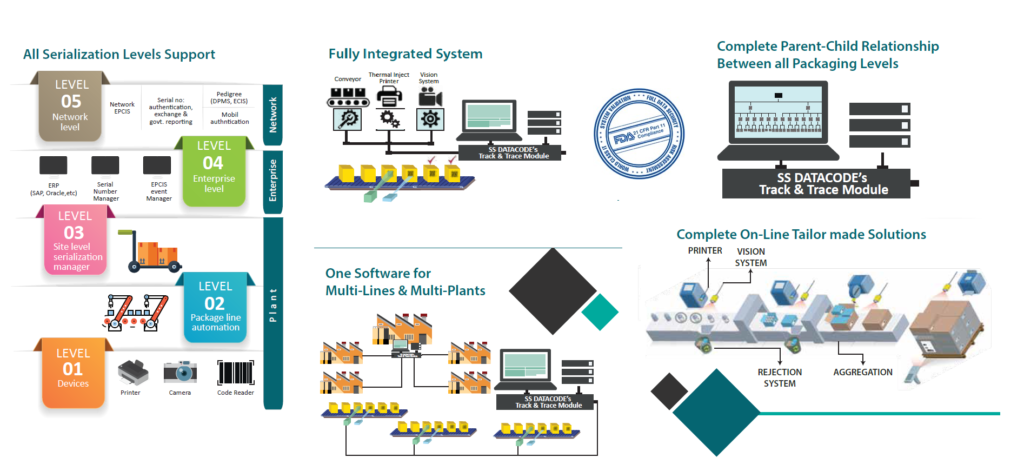
SS DATACODE® offers solutions for serialization and aggregation requirements to pharmaceutical manufacturers and exporters (FDF and API) in India and around the world. DATASOFT™ Track and Trace software offers all Serialization (Level 1 to Level 5) and Aggregation (P, S, T) Levels Support.
For a Demo/Quotation/Inquiry, please reach out to us at [email protected] or click on the Contact Us page.
A glimpse of the benefits offered by our track and trace solution is below: